Lung Caner
Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive diagnostics test, which can help the diagnosis of solid tumors, drug resistance monitoring, as well as drug efficacy evaluation. It’s an effective supplement to the tumor tissue biopsy.
There are several types of liquid biopsy depending on the condition that is being studied.
- In cancer studies, circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and/or cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA) are collected.
- In heart attack diagnosis, circulating endothelial cells (CECs) are sampled.
- In prenatal diagnosis, cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is extracted from maternal blood. Amniotic fluid can also be extracted and analyzed.
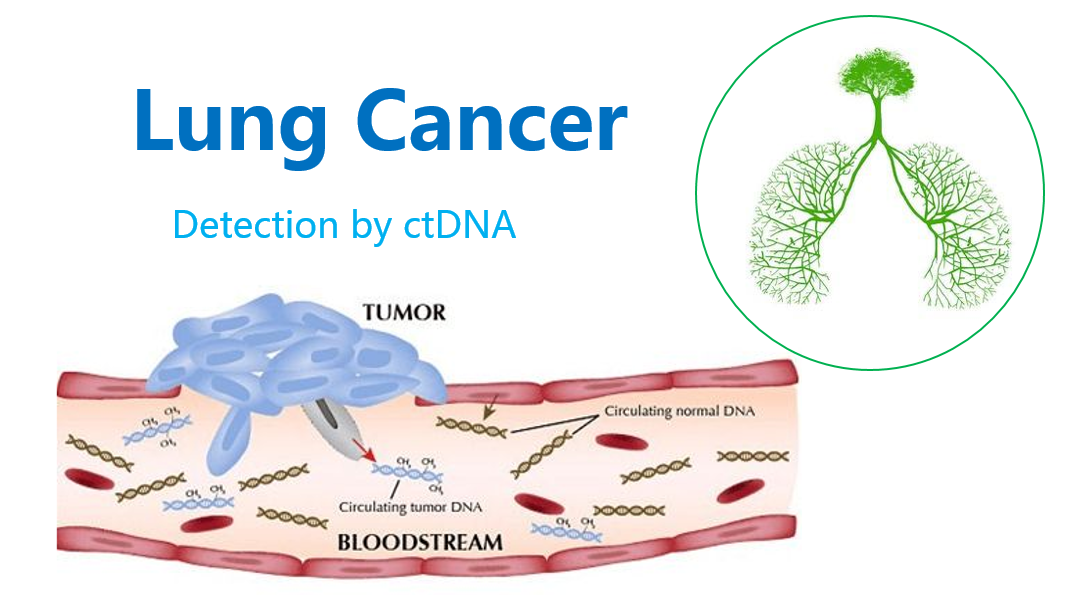
CTCs are tumor cells in the blood circulation system. It contains not only tumor DNA, but also the entire genome, proteome and so on. It is a rich information source for studying tumor tissues. ctDNA refers to DNA fragments of tumor genome (with genomic mutations, deletion, insert, rearrangement, copy number abnormalities, methylation, etc.) in human blood circulation system. The main sources of ctDNA include necrotic tumor cells, apoptotic tumor cells, circulating tumor cells, and exosome excreted by tumor cells. ctDNA is released to the blood when tumor occurrence or metastasis takes place. So as new tumor marker, ctDNA plays an important role in early screening, individualized medication, drug efficacy evaluation and early detection of relapse of tumor. Second-generation sequencing technology-based ctDNA liquid biopsy has high sensitivity and specificity for multi-gene and multi target-point parallel detections.
The advantages of ctDNA detection:
- Non-invasion, low risk, easy sampling, and early diagnosis of cancer compared to the available imaging methods;
- Applicability in detection of various types of tumors regardless of the locations of the tumors;
- Revealing a panorama of genetic mutation in patients without the negative effects of heterogeneous tissue samples;
- Applicability in dynamic monitoring of disease progression and treatment.
Lung cancer is one of the most common type of malignant cancer and also one of the most common causes of cancer-related death. Lung cancer occurs in the bronchial mucosa epithelium, it is also known as bronchial carcinoma. The World Health Organization (WHO) divides lung cancer into four main types by histological classification: small cell lung cancer (SCLC), large cell carcinoma (LCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and adenocarcinoma (ADC).
Liquid biopsy of lung cancer, which is carried out by taking sample of patient’s peripheral blood, is a great method for the detection of lung cancer-related genes, interpretation of lung cancer targeted drugs, detailed understanding of specific genetic mutation in lung cancer patients, and providing patients with personalized medication guidance.
We offer detection of lung cancer at the following sites:
|
Part of the genes for detection |
ALK BRAF EGFR HER2 KRAS MET RET ROS1 CDK4 CDK6 DDR2 FLT1 FGF19 FGR1 FGR2 FGFR1 FGFR2 HRAS KDR MKP2K1 NRAS NTRK1 NTRK2 PIK3CA PTEN RB1 RICTOR SRK11 TP53 TSC1 VEGFA PDGFRA PDGFRB PIK3CA |
Sample requirements:
Blood: 10 mL whole blood, stored and transported in Streck Cell-Free DNA BCT tubes
Plasma and blood cell: After the blood was collected, collect the supernatant and sediment by centrifuging (4℃, 3000g, 10 min) the whole blood, then centrifuge (4℃, 16000g, 10 min) the supernatant to get new supernatant.
Qualified patients for this test:
1. Lung cancer patients who expect to adopt targeted drug therapy.
2. Lung cancer patients who wish to replace a poor therapy with an effective new one.
3. Lung cancer patients who need a new therapy because of drug resistance, recurrence or metastasis of the cancer.
4. Lung cancer patients who need the assessment of postoperative prognosis and cancer recurrent risk.
- 上一篇:Colorectal Caner
- 下一篇:
